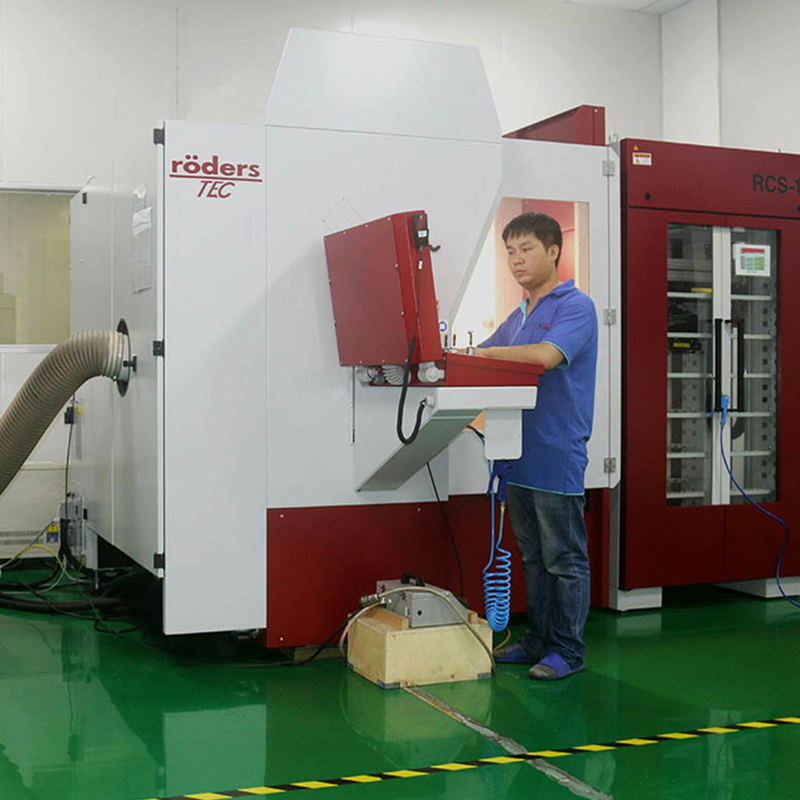
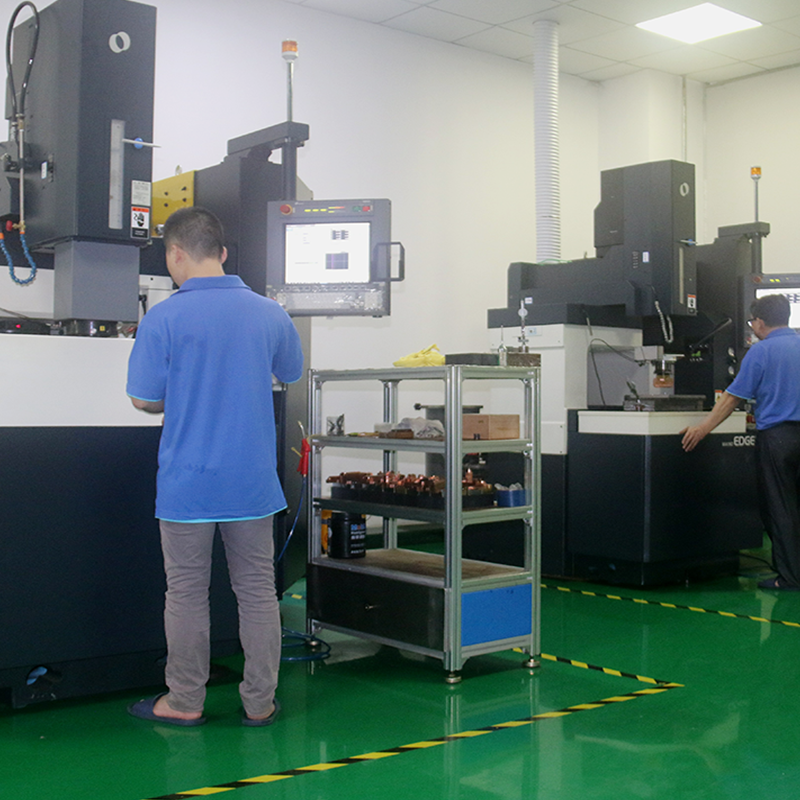
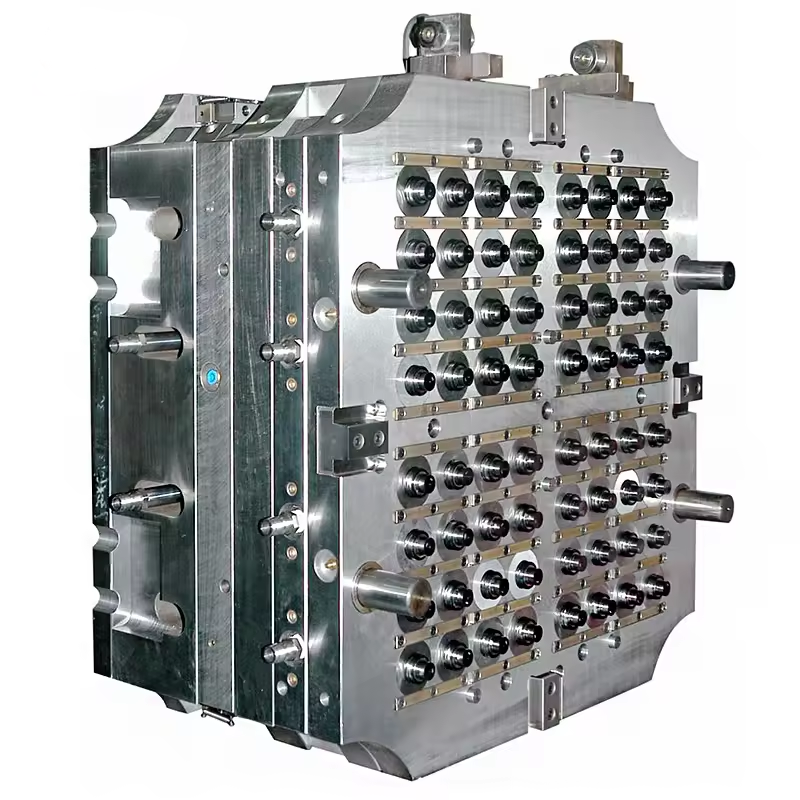
Details:
– Place of Origin:Xiamen, China
– Service:OEM
– Product Material:Steel
– Shaping Mode:Plastic Injection Mould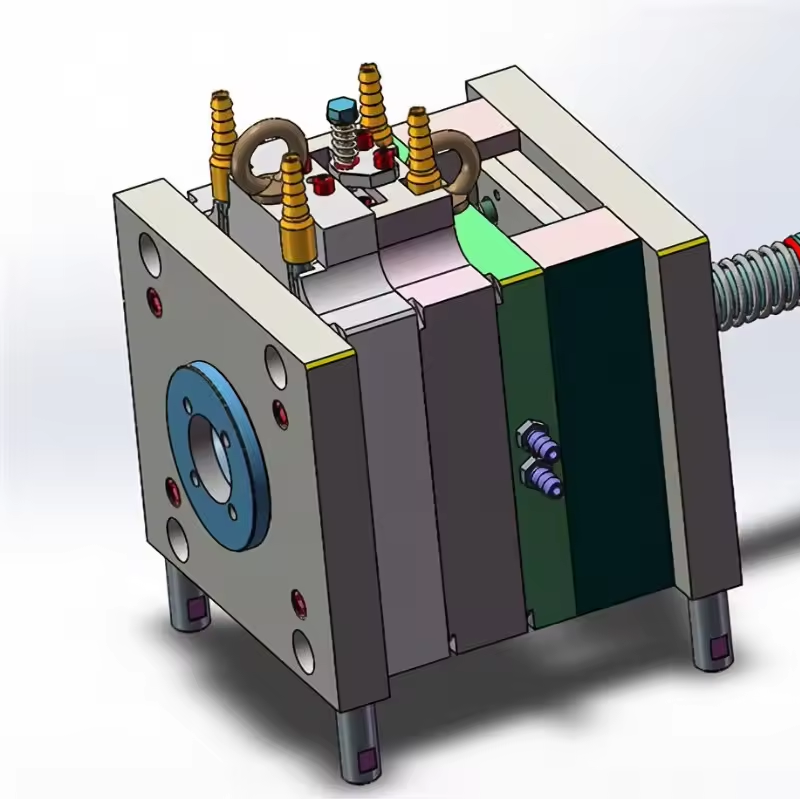
– Injection Material:ABS, PP, PS, PE, PVC, PA6, PA66, etc.
– Mould Material:P20, 718, 738, NAK80, S136, 2738, 2316
– Mold Base:LKM, HASCO, DME, or Chinese Standard
– Tolerance:0.003mm – 0.01mm
– Drawing Format:STEP, STP, IGS, X-T, STL, CAD, PDF, DWG, and others
– Mold Life:500,000 shots
– Runner:Hot Runner or Cold Runner
– Warranty:One Year
– Mold Cavity:Single or Multi-cavity
The Production Process of Plastic Molds for Automotive Parts:
- Design and Engineering
– The process begins with the detailed design and engineering of the mold. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used to create precise mold designs tailored to the specifications of the automotive parts. This phase includes considerations for part geometry, material flow, and mold functionality.
- Material Selection
– High-quality steel or aluminum is selected for mold construction, based on factors such as part complexity, expected production volume, and material properties. The chosen material must withstand the high pressures and temperatures of the injection molding process.
- Machining and Fabrication
– The mold components are machined using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) equipment. This step involves precisely cutting and shaping the mold cavities and cores to achieve the required dimensions and tolerances.
- Assembly
– The machined parts are assembled into a complete mold structure. This includes fitting the mold cavity, core inserts, and any additional components such as cooling channels and ejector systems. The assembly must be meticulously aligned to ensure proper mold function.
- Testing and Calibration
– The assembled mold undergoes rigorous testing to verify its functionality. This includes calibration to ensure that the mold operates correctly and produces parts within specified tolerances. Any necessary adjustments are made to optimize mold performance.
- Final Inspection
– A final inspection is conducted to ensure that the mold meets all design specifications and quality standards. This involves checking for any defects or issues that could affect the mold’s performance during production.
- Delivery and Installation
– Once approved, the completed mold is prepared for delivery. It is carefully packaged and transported to the production facility where it will be installed in the injection molding machine for use in manufacturing automotive parts.
Surface Treatment for Plastic Molds Used in Automotive Parts:
- Polishing
– The mold’s surface is polished to achieve a smooth, high-gloss finish. This step enhances the aesthetic quality of the produced parts and reduces friction during the molding process, which helps in achieving better part release and surface quality.
- Coating
– Protective coatings, such as chrome plating or nitriding, are applied to the mold surface to improve its resistance to corrosion, wear, and abrasion. These coatings extend the mold’s lifespan and ensure consistent part quality by preventing surface degradation.
- Texturing
– Texturing techniques, such as sandblasting or engraving, are used to create specific surface patterns or finishes on the mold. This can impart functional or aesthetic features to the molded parts, such as grip enhancements or design elements.
- Heat Treatment
– The mold undergoes heat treatment processes like annealing or quenching to enhance its hardness and thermal stability. This treatment is crucial for improving the mold’s durability and performance under the high pressures and temperatures of the injection molding process.