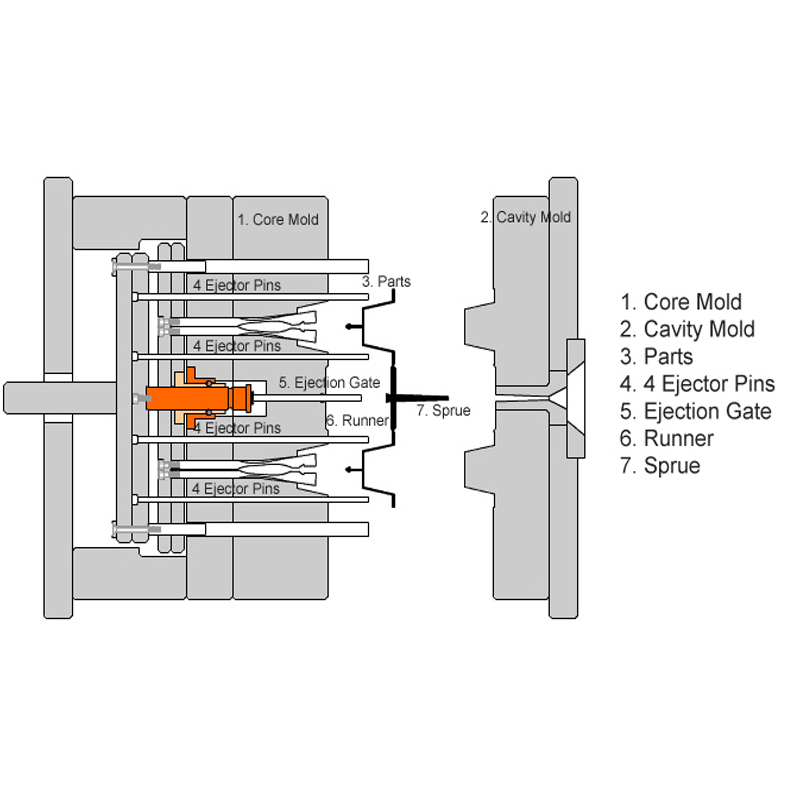
In the field of injection molding, the core and cavity play crucial roles that significantly affect the quality, precision, functionality, and durability of molded components. Their careful design, fabrication, and maintenance are essential for producing consistent, high-quality injection-molded products. This article explores the core and cavity in injection molding, detailing their types, significance, and differences, while also highlighting the advantages offered by our advanced equipment at LSRmold in this area.
Understanding Core and Cavity in Injection Molding
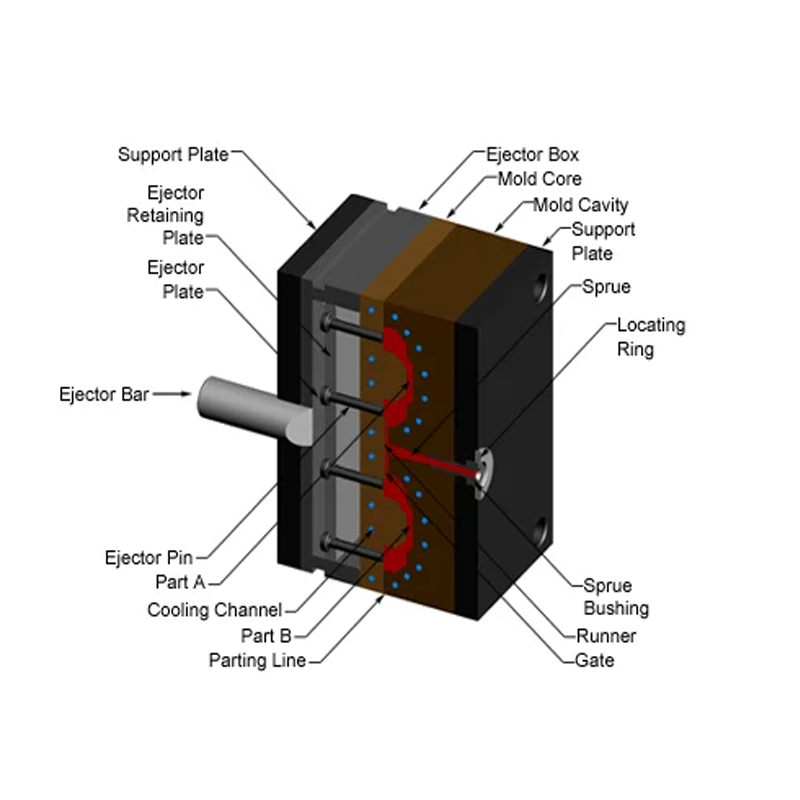
In injection molding, the core and cavity work in tandem to form the desired shape of the molded part. When the mold closes, these components create a cavity that is filled with molten plastic, resulting in the final product. The precision in the design and machining of the core and cavity is critical for ensuring accurate replication of part geometry and optimal molding conditions.
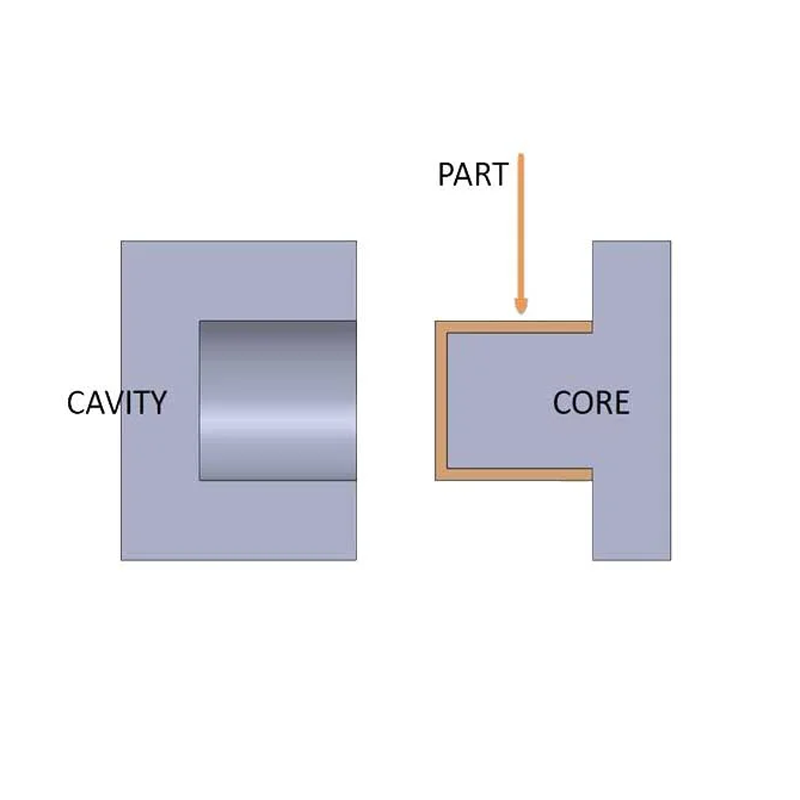
The Role of the Cavity in Injection Molding
The cavity serves as the stationary component of the mold, defining the outer surface of the molded part. It influences the product’s shape, texture, and visual appeal, playing a pivotal role in achieving the desired aesthetics and dimensional accuracy.
The Function of the Core in Injection Molding
The core is the movable element within the mold that shapes the internal characteristics of the part. It is responsible for intricate details, such as holes and recesses, and operates within the mold to establish the specific geometry of the part’s interior, which is essential for its functionality.
Importance of Core and Cavity in Injection Molding
The significance of cores and cavities in the injection molding process can be summarized as follows:
– Shape and Precision: The core and cavity define the shape and dimensions of the molded part, ensuring that the desired features and surface finishes are accurately replicated. Well-engineered cores and cavities enhance the accuracy and repeatability of the molding process.
– Mold Efficiency: The core and cavity are vital to the overall functionality of the mold. They facilitate the proper flow and distribution of molten plastic, ensuring consistent cavity filling. Effective design and machining of these components contribute to improved mold efficiency.
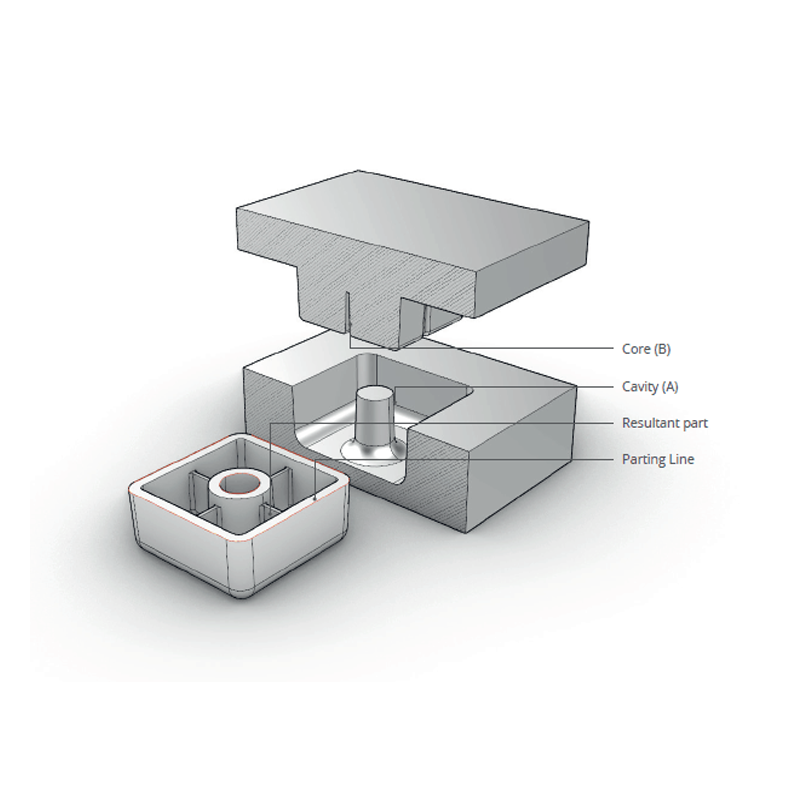
– Durability of Tooling: Given the high levels of stress and thermal cycling encountered during injection molding, cores and cavities must be made from robust, wear-resistant materials. The quality and upkeep of these components are directly related to the longevity and performance of the mold.
– Cooling and Ejection Mechanisms: Cores and cavities also play essential roles in cooling and ejection processes. They typically feature cooling channels that help dissipate heat from the molten material, optimizing solidification times. Additionally, the cavity houses the ejection system, which facilitates the removal of the molded part after cooling.
Types of Mold Cavities and Cores
Injection molds can incorporate various types of cavities and cores, categorized as follows:
- Fixed Cavities and Cores:
– Standard Cavities and Cores: Machined from hardened steel, these components remain fixed throughout production and define the primary shape and features of the part.
– Simple Cavity/Core: Used for parts with straightforward geometries, consisting of a single cavity and core component.
– Multi-Cavity/Core: Configured to produce multiple parts simultaneously in each cycle, enhancing production efficiency.
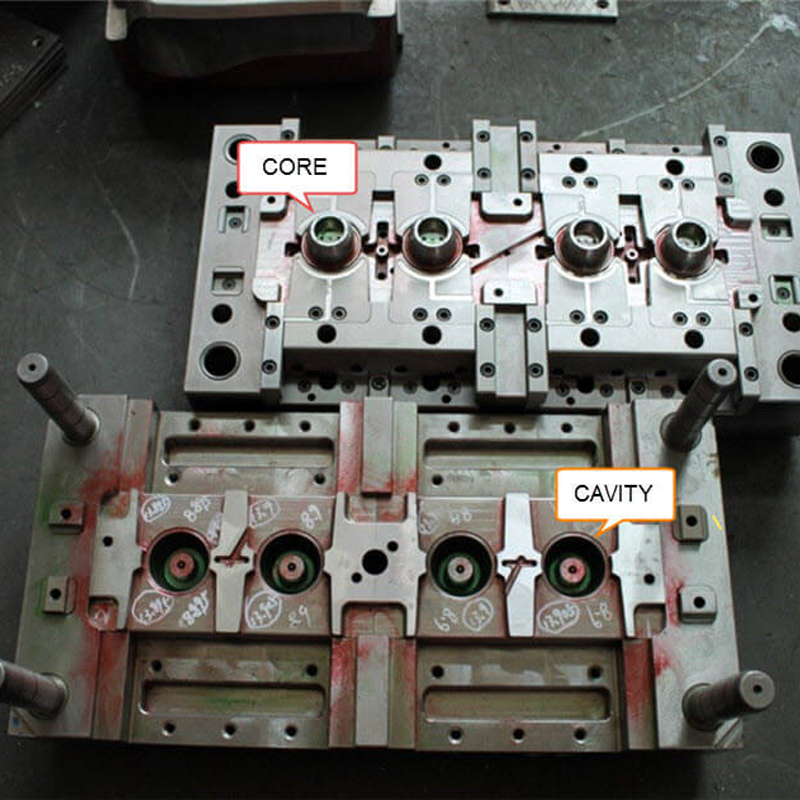
- Interchangeable Cavities and Cores:
– Interchangeable Components: These provide flexibility to produce different parts using the same mold base, allowing for quick adaptations to various designs.
– Replaceable Cavity/Core: These components can be easily swapped out for producing different variations of parts.
– Sliding Cavities and Cores: Capable of movement within the mold, these create complex features such as side holes or threads, essential for intricate part designs.
- Collapsible Core: Designed to create hollow or collapsible sections within the molded part, suitable for complex internal geometries.
- Unscrewing Cavity/Core: Employed for threaded components, these can rotate or unscrew to facilitate the release of threaded parts from the mold.
The selection of specific cavity and core types is dictated by the complexity of the part design, production volume, and other specific requirements, including material flow and ease of assembly.
Distinctions Between Cores and Cavities in Injection Molding
While cores and cavities are both integral to the injection molding process, they serve distinct functions:
- Functionality:
– Cores: Primarily shape the internal features and complex details, defining the internal cavities of the part.
– Cavities: Focus on the external shape, affecting the part’s aesthetics and surface finish.
- Importance:
– Cores: Crucial for the structural integrity and performance of the part, significantly influencing functionality.
– Cavities: Ensure that the final product meets visual quality standards, focusing on aesthetic aspects.
- Design Considerations:
– Cores: Their design must account for ejection mechanisms, cooling, and dimensional stability, possibly including features like slides for undercuts.
– Cavities: Their design is centered on optimal filling, cooling, and venting, with considerations for gating systems and surface textures to ensure effective material flow.
- Placement:
– Cores: Located within the mold to form internal features.
– Cavities: Positioned opposite the cores, shaping the external surfaces of the part.
Advantages of Our Equipment for Mold Making
At LSRmold, we leverage advanced equipment and technology to enhance core and cavity design in our injection molding processes. Our state-of-the-art machinery allows for precision machining and rapid prototyping, ensuring that our molds meet the highest standards of quality and efficiency. Here are some advantages of our equipment:
– Precision Machining: Our advanced CNC machinery ensures high-accuracy machining of cores and cavities, resulting in improved part precision and repeatability.

– Rapid Prototyping Capabilities: We employ cutting-edge prototyping techniques that enable us to quickly develop and test mold designs, reducing lead times and accelerating time-to-market.
– Robust Material Handling: Our equipment is designed to handle a wide range of materials, allowing us to customize molds for specific applications and performance requirements.
– Comprehensive Quality Control: We implement rigorous quality control protocols throughout the manufacturing process, utilizing advanced inspection technologies to guarantee the reliability and durability of our molds.

Conclusion
Cores and cavities are essential elements in injection molding, each contributing significantly to the production of high-quality parts. While cores shape the internal features to ensure functionality, cavities define the external appearance to enhance aesthetics. Their careful design, placement, and functionality are critical for achieving precise and consistent results.
A thorough understanding of the importance and characteristics of cores and cavities is vital for successful injection molding processes. With LSRmold’s commitment to innovation and quality, we are poised to help businesses achieve their manufacturing objectives while delivering outstanding products.