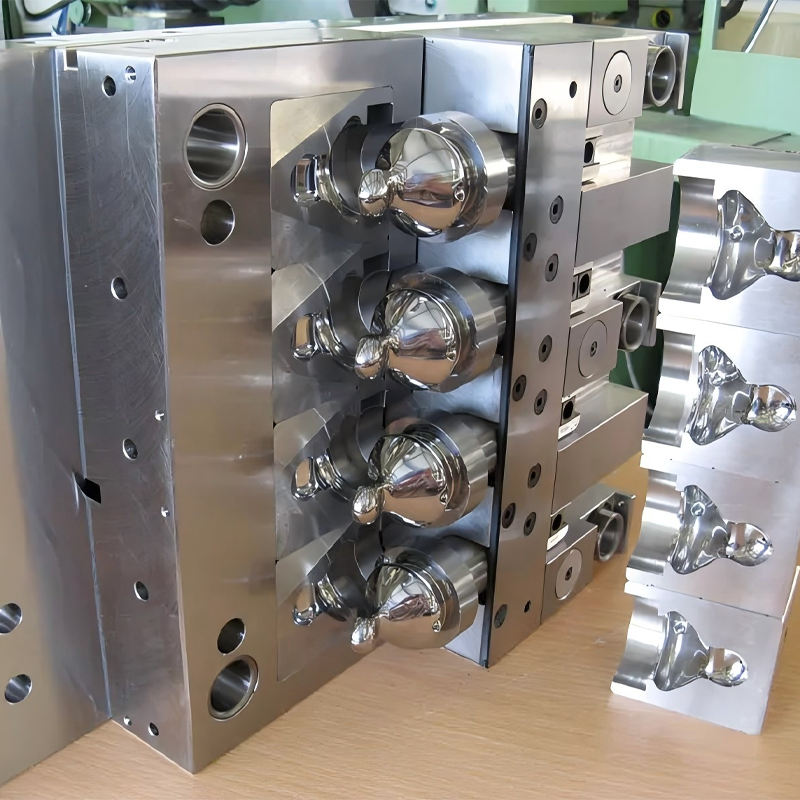
Have you ever wondered how long an injection mold lasts? It’s not a simple question, as numerous factors contribute to its lifespan. Much like predicting when a car might break down, estimating the life of a mold involves several variables. However, we can offer an informed estimate. This estimate helps determine whether a mold is performing optimally or showing signs of early wear.
For instance, if a mold is expected to withstand 250,000 cycles but only lasts for 180,000, it’s a clear indication that it’s underperforming. There are several potential reasons for this—misuse, faulty design, or wear and tear on the mold itself.
So, how can you ensure your molds meet their expected life cycles? It starts with selecting the right mold manufacturer. A skilled manufacturer not only helps you select the ideal mold for your needs but also provides a realistic estimate of its cycle life. Molds can last anywhere from 100,000 cycles to over a million, so understanding what to expect is essential before committing to a mold.
In this article, we’ll explore how to assess and extend the service life of your injection molds.
How Is Injection Mold Life Cycle Measured?
Injection molds are subjected to high-pressure conditions and, over time, experience wear and tear. However, rather than measuring how long a mold runs (in terms of hours or days), the life expectancy of a mold is typically measured by the number of cycles it completes before signs of significant wear emerge.
Cycle time, which refers to how quickly a mold completes one full cycle of production, plays a critical role in determining mold lifespan. Molds with shorter cycle times can complete more cycles per day compared to those with longer cycle times.
A mold’s life is generally measured by the number of cycles completed rather than the time it operates. For instance, if two molds each complete approximately 250,000 cycles before showing signs of wear, they are considered equally effective.
Understanding this concept is crucial for manufacturers. Knowing the mold’s cycle count helps determine whether it’s suitable for your production goals, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
Understanding Mold Service Life with SPI Classifications
The Society of Plastics Industry (SPI) provides a classification system that helps estimate the expected service life of an injection mold based on its cycle performance. This system ranges from Class 101 to Class 105, with each class tailored to different levels of production volume and expected cycle count. Below is an overview of these classifications:
| SPI Mold Class | Typical Production Volume | Expected Cycle Count | Key Features |
| Class 101 | Extremely High Volume | Over 1,000,000 cycles | Made from high-quality materials for high-demand production. Features include guided ejection systems and wear-resistant plates. |
| Class 102 | High Volume | 500,000 to 1,000,000 cycles | Suitable for medium to high production rates, may not require plated cavities or corrosion-resistant temperature control. |
| Class 103 | Medium Volume | Under 500,000 cycles | Designed for medium-volume production, with less stringent requirements. Tool components should be hardened to 28 RC. |
| Class 104 | Low Volume | Fewer than 100,000 cycles | Typically constructed with aluminum or mild steel for cost-effectiveness. Used for short runs or limited production. |
| Class 105 | Prototypes | Fewer than 500 cycles | Cost-effective molds, typically used for prototyping. Made from cast metal or epoxy. |
Factors That Impact Injection Mold Life Cycle
A variety of factors contribute to the longevity of injection molds, beyond just the material and class. By understanding these factors, you can take steps to extend the lifespan of your molds and avoid costly replacements.
Operating Environment: A mold’s environment significantly affects its longevity. Clean, controlled environments extend mold life, while exposure to debris, dust, or corrosive elements can speed up wear.
Time Between Production Cycles: Allowing proper downtime between cycles helps the mold cool down, reducing thermal stress. Continuous use without breaks can cause undue stress and mold damage.
Cycle Time and Speed: Fast injection cycles create more stress on the mold and can reduce its lifespan. Slower cycle times generate less wear, improving the mold’s durability over time.
Material Selection: The type of material used for the mold tooling greatly affects its durability. Steel molds last longer due to their higher resistance to wear and tear, while aluminum molds are more cost-effective but wear out quicker.
Mold Surface Treatment: Applying coatings such as PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) helps reduce friction during part ejection, minimizing wear on the mold surface and extending its life.
Design and Engineering: Proper mold design, especially concerning thermal management and venting, is critical. Mold components like push guides reduce stress and wear, leading to longer mold life.
Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance practices—inspection, cleaning, and repairs—are essential for extending mold service life. Proactive care helps prevent major issues before they cause significant damage.
Common Mold Defects that Impact Service Life
Even the best-maintained molds can suffer from defects that compromise their longevity. Identifying and addressing these defects early is vital to prolonging the mold’s service life.
Flow Lines: These occur when plastic cools unevenly, often due to impurities or inconsistent part thickness. They can lead to poor part quality and mold damage.
Sink Marks: These are depressions or craters caused by uneven cooling, which not only affect the part but also put extra stress on the mold.
Burn Marks: High injection speeds or excessive heating in certain areas of the mold can cause burn marks, damaging the part and mold.
Delamination: This occurs when layers of the plastic separate during molding, which can cause abrasion and mold damage during part ejection.
Flash: Excess plastic that escapes the parting line can create flash, which can adhere to the mold and cause damage if not removed properly.
Effective Strategies to Extend Mold Life
There are several strategies manufacturers can employ to maximize the service life of injection molds, ensuring cost-effective production and minimizing downtime.
| Strategy | Description |
| Material Selection | Choose raw materials that perform well in the injection molding process, contributing to both product quality and mold longevity. |
| Design and Structure | Design molds with robust integrity, ensuring thermal balance, proper gating systems, and efficient cooling to reduce mold stress and wear. |
| Heat Treatment | Use appropriate materials and heat treatments to enhance durability and resistance to wear, corrosion, and deformation. |
| Surface Treatment | Apply coatings or treatments that improve surface smoothness, enhance corrosion resistance, and facilitate easier part ejection. |
| Injection Speed & Pressure | Maintain optimal injection speeds and pressures to prevent undue stress on the mold, reducing the risk of damage and extending its life. |
| Regular Cleaning & Maintenance | Implement routine inspections, cleaning, and repairs to ensure molds are in optimal condition and prevent buildup that could lead to failures. |
Steel vs. Aluminum Molds: Which Is Better for Your Needs?
The choice between steel and aluminum molds directly impacts mold longevity. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Material | Longevity | Best For | Cost |
| Steel | Extremely durable, resists wear and tear better than aluminum. | High-volume, long-term production. | Higher initial cost but better return on investment over time. |
| Aluminum | Shorter lifespan due to softer material, but still suitable for prototyping. | Prototyping, low-volume runs. | Lower initial cost, but may need more frequent replacements in high-volume settings. |
Conclusion
Extending the life of your injection molds is essential for maximizing production efficiency and minimizing costs. With the right design, material selection, and maintenance, you can ensure that your molds serve you for many cycles, ultimately boosting your bottom line. If you’re looking for professional injection molding services and expert advice on mold longevity, LSRmold is here to help. Contact us today for all your mold design and manufacturing needs.